
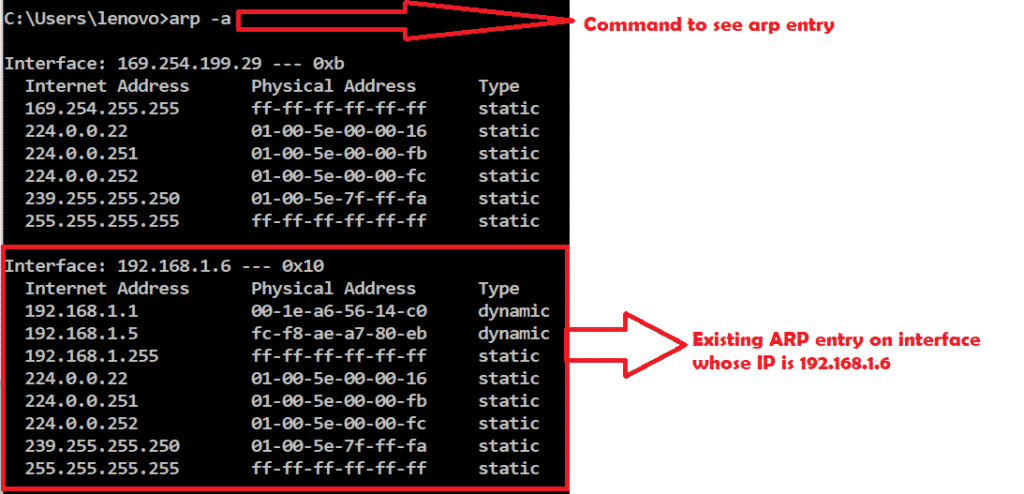
13: Now you can see your roommates or SOs porn browsing habits! Yay! It will then instruct to mirror the traffic.Īfter making your changes to the script, run it, and let's test it out by pinging the gateway again from another machine.įig. It will then set this interface to point the traffic to the domain ID of your VM. It will first select the bridge, then create a mirror for the monitor interface. Super important if you're cloning the traffic on your entire network and sending copies of it to 1 specific interface. Lines 15 & 16 will set those interfaces to promiscuous mode, which will allow it to receive traffic that isn't destined to reach your MAC or IP without dropping it. So, you will wanted to edit line 12 of the script to represent the interface number you configured security onion to listen on For example: $DOM.0 for eth0, $DOM.1 for eth1 So I need to be sending traffic to vif11.0 Well that's the actual interface number of your VM! For example, my VM listens on eth0. But what about the ".number" you see tagged on the end of the vif? 12: The current domain id of my Security Onion VM. Instead you can list the domain ID of each VM with this command:įig. But if you're running dozens of VMs, each with 2~4 interfaces, you're going to have a ridiculous amount of interfaces to comb through. It might be easy to figure out at a glance which VIFs belong to which VM. These "vif", or virtual interfaces, are the actual interfaces of the VM. On your Xen Server host, run ifconfig, and look for an interface named "vif"

If you have no idea what I'm talking about or what it is, I'll explain it real quick. The command 11 returns a numerical value that is then used to identify the domain ID of your virtual interface.
It is the virtual interface label for your VM. This will be the value passed to the ovs-vsctl command. If you don't know what it is, run the command:Īnd find the name-label value there that you set for your VM when you built it. You will have to edit this to match your name-label. On line 11, we query the server for the Security Onion name.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
